

1.5 Pathnames pwd (print working directory) This is very useful if you are lost in the file system. Note: typing cd with no argument always returns you to your homeĭirectory.
Will take you one directory up the hierarchy (back to your home directory). ) means the parent of the current directory, so typing Name of the current directory will save a lot of typing, as we shall see later This may not seem very useful at first, but using (. Means stay where you are (the unixstuff directory). NOTE: there is a space between cd and the dot Make another directory inside the unixstuff directory calledĪs you can see, in the unixstuff directory (and in all otherĭirectories), there are two special directories called (. Type ls to see the contents (which should be empty) Exercise 1a To change to the directory you have just made, type The current working directory may be thought The command cd directory means change the current $ ls 1.3 Changing to a different directory cd (change directory) To see the directory you have just created, type To make a subdirectoryĬalled unixstuff in your current working directory type Will be creating and using in the course of this tutorial. We will now make a subdirectory in your home directory to hold the files you In this tutorial) 1.2 Making Directories mkdir (make directory)
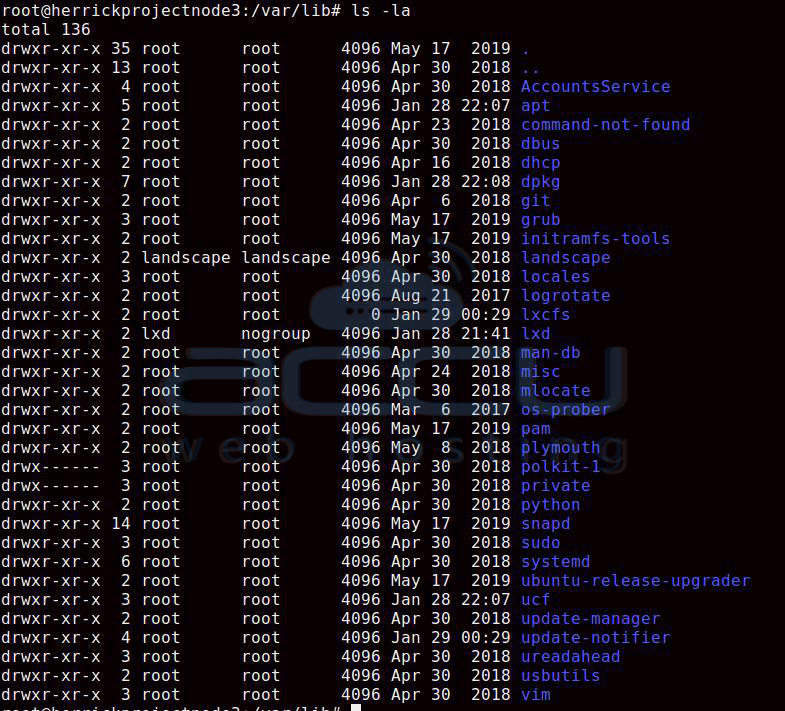
#LIST FILE DETAILS LINUX MANUAL#
There are online manual pages that tell you which options a particular commandĬan take, and how each option modifies the behaviour of the command. The options change the behaviour of the command. Ls is an example of a command which can take options: -a To list all files in your home directory including those whose names begin Them unless you are very familiar with Linux!!! They are hidden because you should not change
To be listed, but only those ones whose name does not begin with a dot (.) Filesīeginning with a dot (.) are known as hidden files and usually contain important Ls does not, in fact, cause all the files in your home directory Alternatively, there may already be some files insertedīy the System Administrator when your account was created.
There may be no files visible in your home directory, in which case, the Linux The ls command lists the contents of your current working directory. To find out what is in your home directory, type Your home directory has the same name as your user-name, for example, unityid,Īnd it is where your personal files and subdirectories are saved. When you first login, your current working directory is your home directory. 1.1 Listing files and directories ls (list) They are included to provide additional information (to you) about what the command is doing. Note: # and text following it are comments and do not need to be entered.
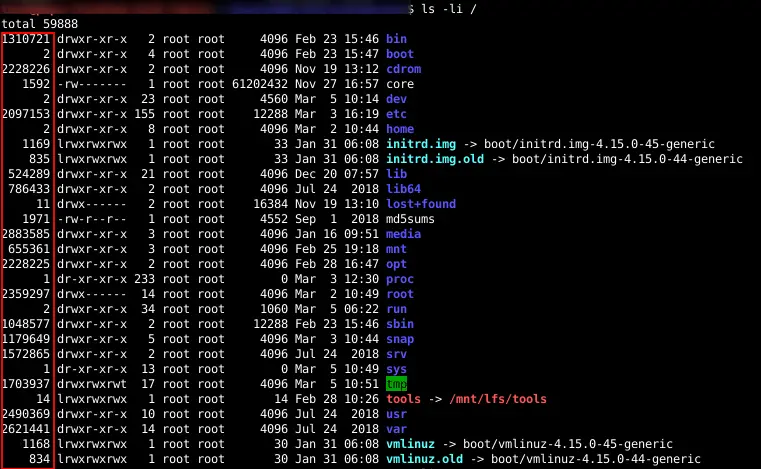
#LIST FILE DETAILS LINUX WINDOWS#
Beware if copying files to a PC, since DOS and Windows The same applies to filenames, so myfile.txt, MyFile.txt and MYFILE.TXT are Note: Linux is case-sensitive, so LS is not the same as ls. Means "at the Linux prompt $, type ls followed by the name of some directory,ĭon't forget to press the key: commands are not sent to the computer Words inserted within square brackets indicate keys.Characters written in italic typewriter font indicate.Characters written in bold typewriter font are commands toīe typed into the computer as they stand.In what follows, we shall use the following typographical conventions: Linux Tutorial One Linux Tutorial One Typographical conventions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
